AI personalization in gaming is transforming how players experience games. Instead of static difficulty modes or pre-set content, modern AI adapts gameplay to each player's behavior, skill, and preferences in real time. This shift not only improves engagement but also drives business growth, with the AI gaming market projected to reach $8.29 billion by 2029. Here’s a quick breakdown of what AI brings to gaming:
- Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment (DDA): Games like Resident Evil tweak challenges in real time to match player performance, keeping the experience balanced.
- Procedural Content Generation (PCG): Titles like No Man’s Sky use AI to create massive, unique game worlds, enabling endless exploration.
- Smarter NPCs: AI-powered characters respond more naturally, enhancing immersion with branching storylines and dynamic interactions.
- Player Retention and Revenue: AI boosts retention by up to 30% and can increase revenue per player by 25%, as seen in games like Marvel Snap.
AI also helps developers scale content creation without expanding teams, making it a game-changer for live-service games. Whether through personalized recommendations, adaptive gameplay, or smarter NPCs, AI is reshaping gaming into a more engaging and profitable industry.
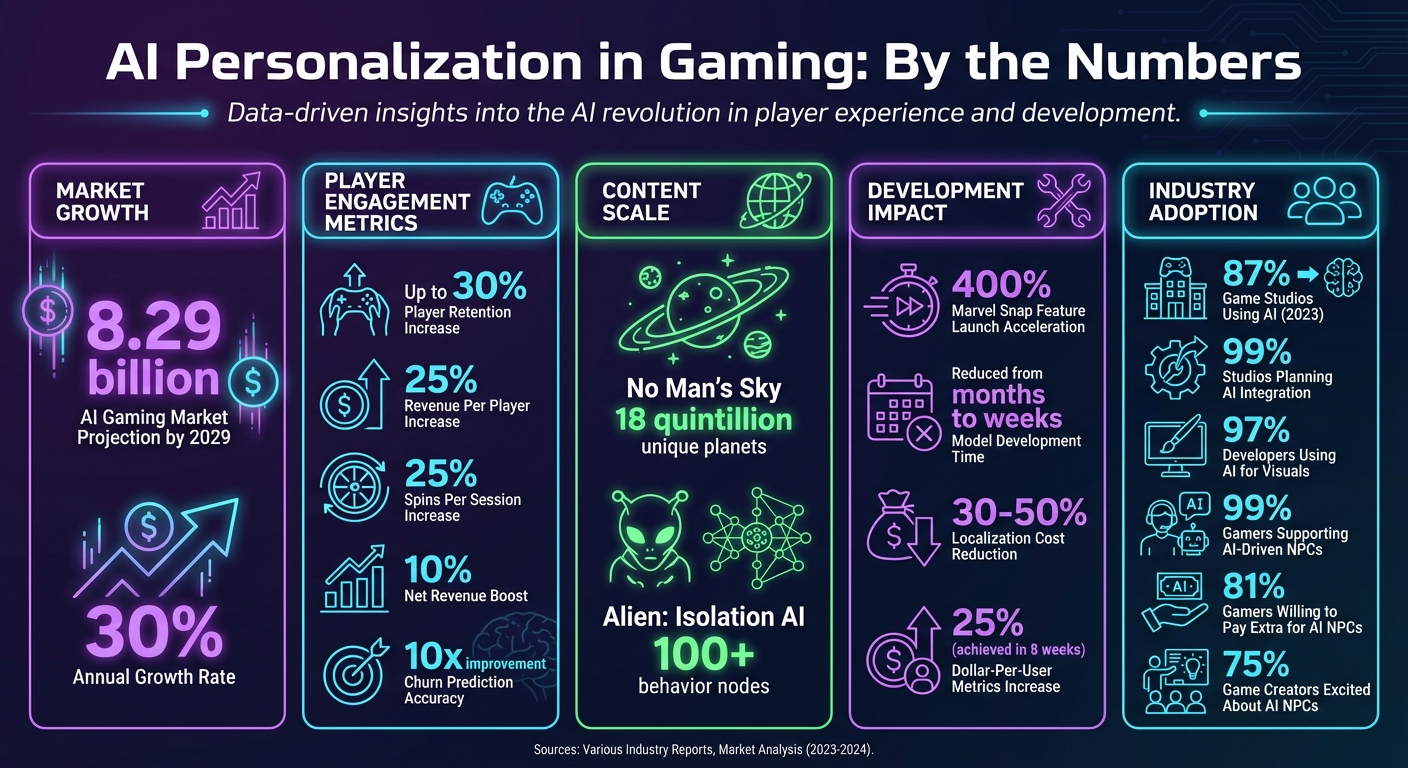
AI Personalization Impact on Gaming: Key Statistics and Market Growth
How AI Increased Game Engagement By 500%
sbb-itb-a759a2a
Case Studies of AI Personalization in Gaming
Building on the AI techniques discussed earlier, these examples highlight how personalization has reshaped gaming experiences across different genres.
No Man's Sky: Procedural Universe Generation
Hello Games created No Man's Sky, a game famous for its 18 quintillion unique planets. By using Procedural Content Generation (PCG) algorithms, the developers crafted planets with distinct environments, structures, and NPC behaviors - all without manually designing each asset. This method allowed the team to scale the game to an extraordinary level while keeping the development team relatively small. Every landing feels like stepping into a new, uncharted world, offering players endless exploration possibilities.
Alien: Isolation: Adaptive Enemy AI
In Alien: Isolation, Creative Assembly designed a dual-layer AI system that makes the xenomorph feel both intelligent and terrifyingly unpredictable. The "Director" AI (Macro-AI) monitors your stress levels using a menace gauge. When tension peaks, it pulls the alien back temporarily, allowing you a brief reprieve before the next hunt begins. Meanwhile, the "Alien" AI (Micro-AI) uses a behavior tree with over 100 nodes, relying on sensors to track sounds like footsteps, gunshots, or even your motion tracker if you're too close (within 1.5 meters).
Andy Bray, Lead AI Designer, described this chilling system as:
Psychopathic serendipity: the alien always finds itself in the right place at the right time.
Although the AI doesn’t learn in real time, it unlocks new behaviors when you repeat certain strategies, giving the impression that it’s adapting to your tactics.
Resident Evil Series: Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment
Capcom’s Resident Evil games, especially the Resident Evil 2 Remake, use Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment (DDA) to maintain a balanced horror experience. The AI tracks player performance and adjusts the game in real time by tweaking enemy health, damage, and behaviors. If you’re cruising through encounters, the game intensifies the challenge. On the flip side, if you’re struggling, it eases the difficulty to prevent frustration. Unlike fixed difficulty modes (Easy, Medium, Hard), DDA ensures the game feels fair while keeping the tension high. This system keeps players immersed by tailoring the challenge to their skill level moment by moment.
| Game | AI Technique | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| No Man's Sky | Procedural Content Generation (PCG) | Endless variety and unique exploration |
| Alien: Isolation | Dual-Layered AI & Menace Gauge | Tense, unpredictable encounters |
| Resident Evil Series | Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment (DDA) | Balanced challenges suited to player skill |
These examples showcase how AI-driven personalization enhances gameplay by creating tailored challenges and fostering a sense of discovery.
Benefits of AI Personalization in Gaming
Improved Player Engagement and Retention
One of the toughest challenges in gaming is keeping players hooked. With countless in-game items and missions to choose from, players can feel overwhelmed. AI-powered recommendation systems simplify this by narrowing down options to just 2–3 choices that align with a player’s preferences. These systems also uncover "golden paths" - optimal sequences of missions or rewards that help players achieve major milestones, like completing the game or earning a platinum ranking. By reducing decision fatigue, these tools minimize drop-offs at frustrating points in the game.
Another game-changer is Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment (DDA), which tweaks challenges in real-time to keep players engaged without making things too easy or too hard. AI also transforms in-game storefronts, showing players cosmetic items or bundles they’re more likely to want, which not only enhances the shopping experience but also boosts sales. The results are impressive: AI personalization can increase player retention by up to 30%, while advanced marketing models improve churn prediction accuracy by over ten times.
Monetization and Scalability
AI personalization doesn’t just keep players engaged - it also opens up new revenue streams. Real-time recommendation engines can increase revenue per player by as much as 25%. A notable example comes from Second Dinner, which revamped Marvel Snap's "Daily Offer Shop" in 2024/2025. By switching from manual updates to a real-time machine learning system powered by Databricks, they launched over 50 new features annually - up from just 10 - and slashed model development time from months to weeks. Ted Li, Associate Director of AI at Second Dinner, highlighted this transformation:
Now, we have the data and tools necessary to personalize gaming and drive revenue.
The impact of these AI systems is clear. For instance, an analysis of 40 billion bets from 32 million players showed that real-time machine learning recommendations led to a 25% increase in spins per session and a 10% boost in net revenue within just a few months. Similarly, Grid Dynamics helped a major video game publisher roll out a reinforcement learning-based personalization platform, achieving a 25% jump in dollar-per-user metrics in only 8 weeks.
AI also addresses the scalability issue through Procedural Content Generation (PCG), which allows studios to create massive game worlds and quests without needing to expand their teams, often utilizing AI content generator tools to maintain high output. This is especially important for live-service games, where players constantly demand fresh content. The AI gaming market reflects this growth, with projections reaching $8.29 billion by 2029, driven by a 30% annual growth rate.
These advancements highlight just how far gaming has come from its earlier, less adaptive methods.
Pre-AI vs. AI-Driven Approaches
| Feature | Pre-AI / Standard Approach | AI-Driven Personalization |
|---|---|---|
| Difficulty | Static settings (Easy/Medium/Hard) | Adaptive; adjusts to real-time skill levels |
| Content | Scripted, linear experiences | Procedural and responsive adventures |
| Storefronts | Static displays or manual updates | Real-time, tailored recommendations |
| Retention | Reactive (e.g., offers after churn) | Proactive (detects fatigue early) |
| Localization | Manual, slow, and costly | Near real-time at 30–50% lower cost |
These shifts signal the dawn of a new era for AI in gaming, paving the way for even more immersive and personalized experiences.
Future of AI Personalization in Game Design
AI-Powered Autonomous NPCs
Game design is stepping into a new era, where non-playable characters (NPCs) are becoming smarter and more lifelike thanks to advanced AI. Using sophisticated models like SLMs and LLMs, NPCs can now engage in unscripted, dynamic conversations that feel organic and personalized to each player. The appeal is undeniable - 99% of gamers support AI-driven NPCs, and 81% are even willing to pay extra for this feature.
One of the most exciting advancements is the integration of memory-first AI, which allows NPCs to recall past interactions with players. This creates a sense of continuity and depth in gameplay. Virginie Mosser, Narrative Director at Ubisoft, expressed the emotional impact of this innovation:
For the first time in my life, I can have a conversation with a character I've created. I've dreamed of that since I was a kid.
The enthusiasm extends to developers as well - three out of four game creators are excited about the potential of AI-powered NPCs.
The technology is evolving quickly. Google DeepMind's SIMA, for example, introduces a new class of generalist agents that can navigate and interact autonomously across diverse 3D environments. These agents act as companions, responding to natural language instructions. Meanwhile, platforms like Inworld AI, Convai, and Charisma.ai are already enabling NPCs to engage in emotionally nuanced conversations. The key challenge now is ensuring these advanced interactions feel seamless and immersive, allowing players to adapt gradually without feeling overwhelmed or disconnected.
These breakthroughs not only transform how NPCs behave but also enhance the creative processes behind their design, empowering developers to push the boundaries of storytelling.
AI-Human Collaboration in Game Development
AI isn't just revolutionizing gameplay - it’s reshaping the way games are created. Instead of manually coding every interaction, developers now guide AI models with detailed backstories and motivations, enabling them to improvise creatively. This shift is becoming the norm: as of 2023, 87% of game studios are using AI in their workflows, and 99% plan to integrate it in the near future.
The benefits are clear. Ubisoft's Ghostwriter, for instance, automates routine dialogue creation, freeing up writers to focus on crafting deeper, more dynamic narratives that evolve based on player choices. This partnership between AI and human creativity enhances both the player experience and the efficiency of game development. Guillemette Picard, Senior Vice President of Production Technology at Ubisoft, highlighted the importance of balance:
Generative AI is only of value if it has value for [developers]. ... developers and their creativity must still drive our projects.
New advancements, like AI "overseer" agents, take player engagement even further. These systems, described by Alex Kearney, Cofounder of Artificial Agency, as "putting a game designer on every player's shoulder", help guide players toward hidden content or create personalized tutorials based on their skill level.
AI tools are also becoming indispensable for visual design. 97% of developers now use AI to generate textures, concept art, and 3D environments on demand using diffusion models. This capability allows studios to produce an endless variety of visuals without needing to expand their teams, addressing the challenges of scaling live-service games.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Main Lessons from Case Studies
Case studies highlight some critical factors that make AI-driven personalization in gaming effective. First, high-quality metadata is essential - going beyond surface-level labels ensures more precise personalization. Second, real-time responsiveness is non-negotiable; systems must maintain latency below 40 milliseconds to keep the experience smooth and immersive.
Take Marvel Snap as an example. The studio behind it, Second Dinner, saw a 400% acceleration in feature launches after implementing real-time machine learning models for personalized recommendations. Another success story comes from Grid Dynamics, which achieved a 25% boost in dollar-per-user metrics in just 8 weeks by rolling out a reinforcement learning–based personalization platform for a top video game publisher.
A recurring theme is the balance between exploration and exploitation. AI needs to recommend familiar, proven content while also introducing players to new experiences to keep things engaging. To ensure these systems deliver real results, developers rely on A/B testing and canary releases. Additionally, AI-powered support systems contribute to operational efficiency, streamlining processes behind the scenes.
Interestingly, these lessons don’t just apply to gaming - they offer a roadmap for content creators looking to integrate AI into their workflows.
AI Tools for Content Creation
The same AI capabilities transforming gaming can also revolutionize content creation. Game studios use AI to scale their content output, and content creators can benefit from similar tools for tasks like automated blog writing, SEO optimization, and multi-language support.
For example, the AI Blog Generator Directory (https://aibloggenerators.com) lists tools designed to simplify workflows for writers and bloggers. These tools handle tasks such as keyword research, analytics integration, and text editing. This mirrors how game developers scale their content efficiently without needing to expand their teams. Similarly, AI localization strategies can cut development costs by 30% to 50%, providing creators with a cost-effective way to maintain quality while reducing production time.
Whether you're creating gaming content or tackling entirely different topics, these AI tools can help you work smarter, not harder.
FAQs
How do games personalize difficulty without feeling unfair?
Games are getting smarter at tailoring difficulty to individual players by adjusting in real-time based on how someone plays. Using AI, games can analyze your actions, skill level, and even how engaged you seem, making tweaks to keep things balanced - challenging but not overwhelming. One technique, dynamic difficulty adjustment (DDA), relies on machine learning to fine-tune the experience, ensuring the challenges feel just right for your skill level. This constant, data-driven tweaking helps create a gaming experience that feels fair, fun, and uniquely suited to each player.
What’s the difference between procedural generation and adaptive AI?
Procedural generation uses algorithms to create game content such as levels or quests. This process often relies on a mix of predefined rules and randomness, allowing for content to be generated automatically with little need for human intervention.
On the other hand, adaptive AI takes things a step further by responding dynamically to player actions and preferences. Through techniques like machine learning, it can adjust elements like storylines, character behaviors, or gameplay mechanics in real time. The result? A gaming experience that feels personalized and tailored to each player.
What data do games need to personalize gameplay in real time?
Games thrive on their ability to adapt to players in real time, and this hinges on collecting and interpreting telemetry data, player behavior signals, decision patterns, and interaction points. By analyzing factors like player actions, choices, engagement levels, and performance metrics, games can fine-tune elements such as content, difficulty, and rewards as the gameplay unfolds. This dynamic approach ensures a more tailored and immersive experience for every player.
